Might be a bonanza
Kendall Square, Cambridge, as seen from across the Charles River in Boston.
Adapted from Robert Whitcomb’s “Digital Diary,’’ in GoLocal24.com
The other week I noted how Greater Boston’s universities and associated institutions have been crucial in enriching the region. We had another example of their ability to spark profitable business ventures with news that the Feds are setting up an “investor catalyst” center at Kendall Square, in Cambridge. Its neighbors, of course, include Harvard and MIT. Kendall Square has become something like the world’s bio-tech capital.
The center will use basic-research findings about such tough diseases as cancers and dementias to create new technologies, medicines and devices, and get them in the market by working with entrepreneurs and financial organizations.
This center, part of the new Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) will probably pump billions into the regional economy over coming years. Perhaps some Rhode Island institutions, especially Brown University and the University of Rhode Island, as well as Lifespan, Care New England and some Ocean State bio-tech businesses – established and startups -- can glom on to some of this activity.
The Worcester area will benefit — e.g., University of Massachusetts Memorial Medical Center, in Worcester — as will institutions farther away, such as Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, in Labanon, N.H., and Maine Medical Center, in Portland.
Judith Graham: With the arrival of Aduhelm, what is 'mild cognitive impairment'?
19th Century drawing of man with dementia
The approval of a controversial new drug for Alzheimer’s disease, Aduhelm, made by Cambridge, Mass.-based Biogen, is shining a spotlight on mild cognitive impairment — problems with memory, attention, language or other cognitive tasks that exceed changes expected with normal aging.
(Kendall Square in Cambridge, Biogen’s neighborhood, has become arguably the bio-tech center of the world.)
After initially indicating that it could be prescribed to anyone with dementia, the Food and Drug Administration now specifies that the prescription drug be given only to individuals with mild cognitive impairment or early-stage Alzheimer’s, the groups in which the medication was studied.
Yet this narrower recommendation raises questions. What does a diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment mean? Is Aduhelm appropriate for all people with mild cognitive impairment, or only some? And who should decide which patients qualify for treatment: dementia specialists or primary-care physicians?
Controversy surrounds Aduhelm because its effectiveness hasn’t been proved, its cost is high (an estimated $56,000 a year, not including expenses for imaging and monthly infusions), and its potential side-effects are significant (41 percent of patients in the drug’s clinical trials experienced brain swelling and bleeding).
Furthermore, an FDA advisory committee strongly recommended against Aduhelm’s approval, and Congress is investigating the process leading to the FDA’s decision. Medicare is studying whether it should cover the medication, and the Department of Veterans Affairs has declined to do so under most circumstances.
Clinical trials for Aduhelm excluded people over age 85; those taking blood thinners; those who had experienced a stroke; and those with cardiovascular disease or impaired kidney or liver function, among other conditions. If those criteria were broadly applied, 85 percent of people with mild cognitive impairment would not qualify to take the medication, according to a new research letter in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
Given these considerations, carefully selecting patients with mild cognitive impairment who might respond to Aduhelm is “becoming a priority,” said Dr. Kenneth Langa, a professor of medicine, health management and policy at the University of Michigan.
Dr. Ronald Petersen, who directs the Mayo Clinic’s Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center, said, “One of the biggest issues we’re dealing with since Aduhelm’s approval is, ‘Are appropriate patients going to be given this drug?’”
Here’s what people should know about mild cognitive impairment based on a review of research studies and conversations with leading experts:
Basics. Mild cognitive impairment is often referred to as a borderline state between normal cognition and dementia. But this can be misleading. Although a significant number of people with mild cognitive impairment eventually develop dementia — usually Alzheimer’s disease — many do not.
Cognitive symptoms — for instance, difficulties with short-term memory or planning — are often subtle but they persist and represent a decline from previous functioning. Yet a person with the condition may still be working or driving and appear entirely normal. By definition, mild cognitive impairment leaves intact a person’s ability to perform daily activities independently.
According to an American Academy of Neurology review of dozens of stuies, published in 2018, mild cognitive impairment affects nearly 7 percent of people ages 60 to 64, 10 percent of those 70 to 74 and 25 percent of 80-to-84-year-olds.
Causes. Mild cognitive impairment can be caused by biological processes (the accumulation of amyloid beta and tau proteins and changes in the brain’s structure) linked to Alzheimer’s disease. Between 40 percent and 60 percent of people with mild cognitive impairment have evidence of Alzheimer’s-related brain pathology, according to a 2019 review.
But cognitive symptoms can also be caused by other factors, including small strokes; poorly managed conditions, such as diabetes, depression and sleep apnea; responses to medications; thyroid disease; and unrecognized hearing loss. When these issues are treated, normal cognition may be restored or further decline forestalled.
Subtypes. During the past decade, experts have identified four subtypes of mild cognitive impairment. Each subtype appears to carry a different risk of progressing to Alzheimer’s disease, but precise estimates haven’t been established.
People with memory problems and multiple medical issues who are found to have changes in their brain through imaging tests are thought to be at greatest risk. “If biomarker tests converge and show abnormalities in amyloid, tau and neuro-degeneration, you can be pretty certain a person with MCI has the beginnings of Alzheimer’s in their brain and that disease will continue to evolve,” said Dr. Howard Chertkow, chairperson for cognitive neurology and innovation at Baycrest, an academic health-sciences center in Toronto that specializes in care for older adults.
Diagnosis. Usually, this process begins when older adults tell their doctors that “something isn’t right with my memory or my thinking” — a so-called subjective cognitive complaint. Short cognitive tests can confirm whether objective evidence of impairment exists. Other tests can determine whether a person is still able to perform daily activities successfully.
More sophisticated neuropsychological tests can be helpful if there is uncertainty about findings or a need to better assess the extent of impairment. But “there is a shortage of physicians with expertise in dementia — neurologists, geriatricians, geriatric psychiatrists” — who can undertake comprehensive evaluations, said Kathryn Phillips, director of health services research and health economics at the University of California-San Francisco School of Pharmacy.
The most important step is taking a careful medical history that documents whether a decline in functioning from an individual’s baseline has occurred and investigating possible causes such as sleep patterns, mental health concerns and inadequate management of chronic conditions that need attention.
Mild cognitive impairment “isn’t necessarily straightforward to recognize, because people’s thinking and memory changes over time [with advancing age] and the question becomes ‘Is this something more than that?’” said Dr. Zoe Arvanitakis, a neurologist and director of Rush University’s Rush Memory Clinic, in Chicago.
More than one set of tests is needed to rule out the possibility that someone performed poorly because they were nervous or sleep-deprived or had a bad day. “Administering tests to people over time can do a pretty good job of identifying who’s actually declining and who’s not,” Langa said.
Progression. Mild cognitive impairment doesn’t always progress to dementia, nor does it usually do so quickly. But this isn’t well understood. And estimates of progression vary, based on whether patients are seen in specialty dementia clinics or in community medical clinics and how long patients are followed.
A review of 41 studies found that 5 percent of patients treated in community settings each year went on to develop dementia. For those seen in dementia clinics — typically, patients with more serious symptoms — the rate was 10 percent. The American Academy of Neurology’s review found that after two years 15 percent of patients were observed to have dementia.
Progression to dementia isn’t the only path that people follow. A sizable portion of patients with mild cognitive impairment — from 14 percent to 38 percent — are discovered to have normal cognition upon further testing. Another portion remains stable over time. (In both cases, this may be because underlying risk factors — poor sleep, for instance, or poorly controlled diabetes or thyroid disease — have been addressed.) Still another group of patients fluctuate, sometimes improving and sometimes declining, with periods of stability in between.
“You really need to follow people over time — for up to 10 years — to have an idea of what is going on with them,” said Dr. Oscar Lopez, director of the Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center at the University of Pittsburgh.
Specialists versus generalists. Only people with mild cognitive impairment associated with Alzheimer’s should be considered for treatment with Aduhelm, experts agreed. “The question you want to ask your doctor is, ‘Do I have MCI [mild cognitive impairment] due to Alzheimer’s disease?’” Chertkow said.
Because this medication targets amyloid, a sticky protein that is a hallmark of Alzheimer’s, confirmation of amyloid accumulation through a PET scan or spinal tap should be a prerequisite. But the presence of amyloid isn’t determinative: One-third of older adults with normal cognition have been found to have amyloid deposits in their brains.
Because of these complexities, “I think, for the early rollout of a complex drug like this, treatment should be overseen by specialists, at least initially,” said Petersen of the Mayo Clinic. Arvanitakis of Rush University agreed. “If someone is really and truly interested in trying this medication, at this point I would recommend it be done under the care of a psychiatrist or neurologist or someone who really specializes in cognition,” she said.
Judith Graham is a Kaiser Health News reporter.
Judith Graham: khn.navigatingaging@gmail.com, @judith_graham
Harris Meyer: Amidst intense controversy, FDA approves Biogen’s Alzheimer's drug
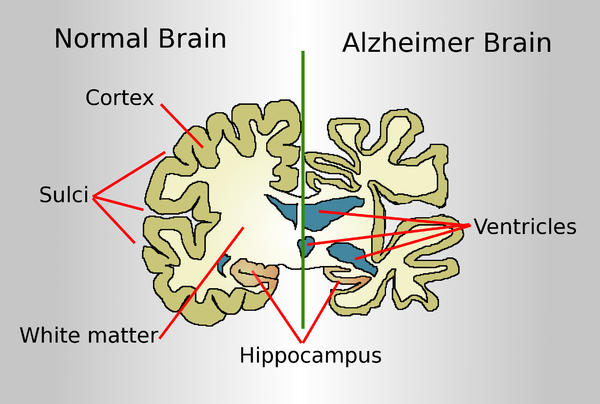
Drawing comparing a normal aged brain (left) and the brain of a person with Alzheimer's (right). Characteristics that separate the two are pointed out.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, a drug developed by Biogen, which is based in Cambridge’s Kendall Square neighborhood. But the approval highlights a deep division over the drug’s benefits as well as criticism about the integrity of the FDA approval process.
The approval of aducanumab came despite a near-unanimous rejection of the product by an FDA advisory committee of outside experts in November. Doubts were raised when, in 2019, Biogen halted two large clinical trials of the drug after determining it wouldn’t reach its targets for efficacy. But the drugmaker later revised that assessment, stating that one trial showed that the drug reduced the decline in patients’ cognitive and functional ability by 22 percent.
Some FDA scientists in November joined with the company to present a document praising the intravenous drug. But other FDA officials and many outside experts say the evidence for the drug is shaky at best and that another large clinical trial is needed. A consumer advocacy group has called for a federal investigation into the FDA’s handling of the approval process for the product.
A lot is riding on the drug for Biogen. It is projected to carry a $50,000-a-year price tag and would be worth billions of dollars in revenue to the Cambridge company.
The FDA is under pressure because an estimated 6 million Americans are diagnosed with Alzheimer’s, a debilitating and ultimately fatal form of dementia, and there are no drugs on the market to treat the underlying disease. Although some drugs slightly mitigate symptoms, patients and their families are desperate for a medication that even modestly slows its progression.
Aducanumab helps the body produce antibodies that remove amyloid plaques from the brain, which has been associated with Alzheimer’s. It’s designed for patients with mild-to-moderate cognitive decline from Alzheimer’s, of which there are an estimated 2 million Americans. But it’s not clear whether eliminating the plaque improves brain function in Alzheimer’s patients. So far, nearly two dozen drugs based on the so-called amyloid hypothesis have failed in clinical trials.
Besides questions about whether the drug works, there also are safety issues. More than one-third of patients in one of the trials experienced brain swelling and nearly 20 percenty had brain bleeding, though those symptoms generally were mild and controllable. Because of those risks, patients receiving aducanumab have to undergo regular brain monitoring through expensive PET scans and MRI tests.
Some physicians who treat Alzheimer’s patients say they won’t prescribe the drug even if it’s approved.
“There’s a lot of hope among my patients that this is going to be a game changer,” said Dr. Matthew Schrag, an assistant professor of neurology at Vanderbilt University. “But the cognitive benefits of this drug are quite small, we don’t know the long-term safety risks, and there will be a lot of practical issues in deploying this therapy. We have to wait until we’re certain we’re doing the right thing for patients.”
Many aspects of aducanumab’s journey through the FDA approval process have been unusual. It’s “vanishingly rare” for a drug to continue on toward approval after its clinical trial was halted because unfavorable results showed that further testing was futile, said Dr. Peter Lurie, president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest and a former FDA associate commissioner. And it’s “mind-boggling,” he added, for the FDA to collaborate with a drugmaker in presenting a joint briefing document to an FDA advisory committee.
“A joint briefing document strikes me as completely inappropriate and an abdication of the FDA’s claim to being the best regulatory agency in the world,” Lurie said.
Three FDA advisory committee members who voted in November against approving the drug wrote in a recent JAMA commentary that the FDA’s “unusual degree of collaboration” with Biogen led to criticism that it “potentially compromised the FDA’s objectivity.” They cast doubt on both the drug’s safety and the revised efficacy data.
The FDA and Biogen declined to comment for this article.
Despite the uncertainties, the Alzheimer’s Association, the nation’s largest Alzheimer’s patient advocacy group, has pushed hard for FDA approval of aducanumab, mounting a major print and online ad campaign last month. The “More Time” campaign featured personal stories from patients and family members. In one ad, actor Samuel L. Jackson posted on Twitter, “If a drug could slow Alzheimer’s, giving me more time with my mom, I would have read to her more.”
But the association has drawn criticism for having its representatives testify before the FDA in support of the drug without disclosing that it received $525,000 in contributions last year from Biogen and its partner company, Eisai, and hundreds of thousands of dollars more in previous years. Other people who testified stated upfront whether or not they had financial conflicts.
Dr. Leslie Norins, founder of a group called Alzheimer’s Germ Quest that supports research, said the lack of disclosure hurts the Alzheimer’s Association’s credibility. “When the association asks the FDA to approve a drug, shouldn’t it have to reveal that it received millions of dollars from the drug company?” he asked.
But Joanne Pike, the Alzheimer’s Association’s chief strategy officer, who testified before the FDA advisory committee about aducanumab without disclosing the contributions, denied that the association was hiding anything or that it supported the drug’s approval because of the drugmakers’ money. Anyone can search the association’s website to find all corporate contributions, she said in an interview.
Pike said her association backs the drug’s approval because its potential to slow patients’ cognitive and functional decline offers substantial benefits to patients and their caregivers, its side effects are “manageable,” and it will spur the development of other, more effective Alzheimer’s treatments.
“History has shown that approvals of first drugs in a category benefit people because they invigorate the pipeline,” she said. “The first drug is a start, and the second and third and fourth treatment could do even better.”
Lurie disputed that. He said lowering the FDA’s standards and approving an ineffective or marginally effective drug merely encourages other manufacturers to develop similar, “me too” drugs that also don’t work well.
Anne Saint says she wouldn’t have risked putting her husband, Mike Saint, on the new Alzheimer’s drug aducanumab because of safety issues. Mike died in September at age 71. (MOLLY SAINT)
The Public Citizen Health Research Group, which opposes approval of aducanumab, has called for an investigation of the FDA’s “unprecedented and inappropriate close collaboration” with Biogen. It asked the inspector general of the Department of Health and Human Services to probe the approval process, which that office said it would consider.
The group also urged the acting FDA commissioner, Dr. Janet Woodcock, to remove Dr. Billy Dunn, an aducanumab advocate who testified about it to the advisory committee, from his position as director of the FDA’s Office of Neuroscience and hand over review of the drug to staffers who weren’t involved in the Biogen collaboration.
Woodcock refused, saying in a letter that FDA “interactions” with drugmakers make drug development “more efficient and more effective” and “do not interfere with the FDA’s independent perspective.”
Although it would be unusual for the FDA to approve a drug after rejection by an FDA advisory committee, it’s not unprecedented, Lurie said. Alternatively, the agency could approve it on a restricted basis, limiting it to a segment of the Alzheimer’s patient population and/or requiring Biogen to monitor patients.
“That will be tempting but shouldn’t be the way the problem is solved,” he said. “If the product doesn’t work, it doesn’t work. Once it’s on the market, it’s very difficult to get it off.”
If the drug is approved, Alzheimer’s patients and their families will have to make a difficult calculation, balancing the limited potential benefits with proven safety issues.
Anne Saint, whose husband, Mike, had Alzheimer’s for a decade and died in September at age 71, said that based on what she’s read about aducanumab, she wouldn’t have put him on the drug.
“Mike was having brain bleeds anyway, and I wouldn’t have risked him having any more side effects, with no sure positive outcome,” said Saint, who lives in Franklin, Tenn. “It sounds like maybe that drug’s not going to work, for a lot of money.”
Their adult daughter, Sarah Riley Saint, feels differently. “If this is the only hope, why not try it and see if it helps?” she said.
Harris Meyer is a Kaiser Health News reporter.
Boeing and MIT announce Kendall Square project
At Kendall Square, in Cambridge.
From the New England Council (newenglandcouincil.com)
"Boeing Co. and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) recently announced plans to open a new Boeing Aerospace & Autonomy Center in Cambridge’s Kendall Square neighborhood, making Boeing the first tenant of MIT’s long-planned Kendall Square Initiative. Under the new agreement, Boeing Co. will occupy about one-third of the 343,000-square-foot office building which will house the company’s recenlty-purchased subsidiary, Aurora Flight Sciences, a Virginia-based company that specializes in the design and construction of advanced unmanned systems and aerospace vehicles. The new center will focus on designing, building, and flying autonomous aircraft and developing enabling technologies.
The agreement builds on a century-long research relationship that Boeing and MIT established with the overarching goal of advancing aerospace innovation. Earlier this year, the company announced that it will serve as lead donor for a new $18 million wind tunnel on campus.
MIT Provost Martin Schmidt said, “It’s fitting that Boeing will join the Kendall/MIT innovation family. Our research interests have been intertwined for over 100 years, and we’ve worked together to advance world-changing aerospace technologies and systems. MIT’s Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics is the oldest program of its kind in the United States, and excels at its mission of developing new air transportation concepts, autonomous systems, and small satellites through an intensive focus on cutting-edge education and research. Boeing’s presence will create an unprecedented opportunity for new synergies in this industry.”