Llewellyn King: Thank God for electricity, especially now; but the grid is always under threat
WEST WARWICK, R.I.
Nothing will be the same again
Those are words that that challenge the heart and the imagination. The heart because, as in a death or the loss of a job, some things will be very missed. The imagination because it needs inspired speculation to know how the present crisis will reshape the way we live; how we are governed, how we educate, how we do business and how we play.
Some losses are somewhat predictable. Most of us may never sit in a movie theater again because there may be no movie theaters. They were already having a hard time with the competition from streaming services, now many may just not reopen. Question: What will be done with those buildings? They are mostly part of shopping centers where many of the tenants for restaurants and specialty shops will also go out of business.
Here’s my answer: In that glorious time when we have licked COVID-19, many new entrepreneurs will get their start in those empty shells. A myriad of yet-unknown businesses will crop up, coming out of these times of ultra-difficulty. Failing shopping centers offer habitat to startups.
We are in a state of war and in war, despite its horror, there is invention. As we try to defeat this pandemic, there will be inventions aplenty.
War has always spurred creativity, in art and in science, and in its aftermath, a time of optimism and opportunity. Catastrophe shakes up society and reorients it. There is a high price but a great reward
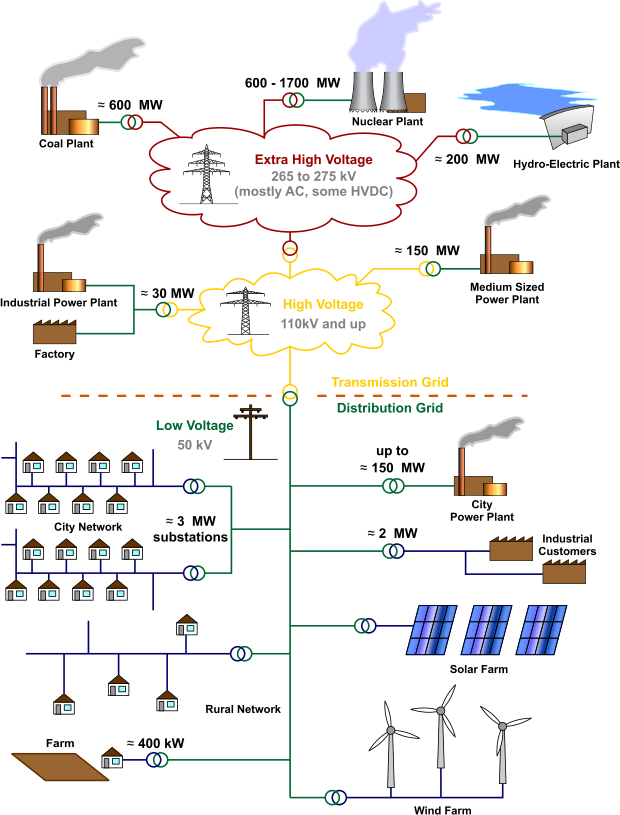
Needs must, there will be a re-evaluation of values and the goods and services which are essential. High on that list will be electricity. Over and over again we will be asking ourselves if the electric grid is safe and if so, how safe?
As Morgan O’Brien, co-founder of Nextel and now CEO of Anterix, which offers utilities secure communications systems, told me, “The coronavirus pandemic is putting more stress on the infrastructure which keeps our society functioning. Critical infrastructure like the electric grid will be more stressed as it is the essential lifeline for Americans sheltering in place.”
A loss of all or part of the grid is an existential fear that has had experts worried since the first computer hackers had a go at it. Utility presidents have told me that it is grid security that keeps them awake at night. It should. CPS Energy, the utility in San Antonio, gets more than 2 million hits a day, I believe.
Late last year the president’s National Infrastructure Advisory Council warned strongly of the dangers of cyberattack. It said the electric utility industry is good at tackling small, short-term outages but it is essentially unprepared for catastrophic outages lasting a long time.
Earlier this year James Woolsey, a former CIA director and an honorary co-chair of the Secure the Grid Coalition, wrote to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission demanding it order more physical security for transformers, pylons, etc. Woolsey cited a lack of improved physical security since that became an issue with the sophisticated disabling of Pacific Gas & Electric’s substation in Metcalf, Calif., in 2013.
John Savage, professor emeritus of computer science at Brown University, who is writing a book on cybersecurity, raises a less-mentioned dimension of threat to the grid: the role of GPS. With the advent of global positioning satellites, he explained, the utility industry switched from using atomic clocks to using GPS timing as the basis for its nationwide synchronization.
Savage told me, “Dependence on GPS for timing is a security risk. If GPS timing signals are distorted or lost, serious damage may be done to the grid.
“GPS signals can be lost due to a local jamming, blackouts, produced by a solar flare, or spoofing. A GPS anomaly alone or a cyberattack combined with one can cascade and bring down a large portion of the grid for an extended period of time.”
Gen. James Jones, a retired Marine commandant and NATO commander, told me, “For the past several years, I have been preoccupied by the proximity of threats, particularly in the cyber realm.”
Much will change, but the need for reliable electricity will remain paramount.
Llewellyn King is executive producer and host of White House Chronicle, on PBS. His email is llewellynking1@gmail.com, and he’s based in Rhode Island and Washington, D.C.
Llewellyn King: We must prepare for cyberattacks on our infrastructure
"The Bridge'' (encaustic painting by Nancy Whitcomb.
WEST WARWICK, R.I.
War always goes for the infrastructure: Take out the bridges, cut off the electricity and water supplies. All that used to be done with artillery, tanks and bombs from above.
Going forward, it will be done by computers: cyberwar.
Every day the early skirmishes -- the tryout phase, if you will – are taking place. There are tens of thousands of probes of U.S. infrastructure by potential enemies, known and unknown, state and non-state. A few get through the defenses.
Jeremy Samide, chief executive officer of Stealthcare, a company which seeks to improve cyberdefenses for a diverse set of U.S. companies, sees the cyber battlefield starkly. He says the threat is very real; and he puts the threat of serious attack at 83 percent.
As Samide looks out across the United States from his base in Cleveland, he sees probes, the term of art for incoming cyberattacks, like an endless rain of arrows. Some, he says, will get through and the infrastructure is always at risk.
Director of National Intelligence Dan Coats issued a warning in July that the alarms for our digital infrastructure are “blinking.” He compared the situation to that in the country before the 9/11 terrorist attacks. The situation, he told the Hudson Institute in a speech, is “critical.” Coats singled out Russia as the most active of the probers of U.S. infrastructure.
Samide says probing can come from anywhere and Russia may be the most active of the cyber adventurers.
A common scenario, he says, is that the electric grid is target one. But considerable devastation could come from attacking banking, communications, transportation or water supply.
Retired Army Gen. David Petraeus, a former director of the CIA and current chairman of KKR Global Institute, in an article coauthored with Kiran Sridhar and published in Politico on Sept. 5, urges the creation of a new government agency devoted to cybersecurity.
Samide and others endorse this and worry that the government has much vital material spread across many agencies and not coordinated. Behind Petraeus’s thinking is one of the lessons of 9/11: Government departments aren’t good at sharing information.
Conventional wisdom has it that the electric grid is super-vulnerable. But Politico’s cybersecurity reporter David Perera, who consulted experts on the feasibility of taking down the grid, somewhat demurs. In a Politico article, he concluded that the kind of national blackout often theorized isn’t possible because of the complexity of the engineering in the grid and its diversity.
The difficulty, according to Perera, is for the intruder to drill down into the computer-managed engineering systems of the grid and attack the programable controllers, also known as industrial control systems -- the devices that run things, such as by moving load, closing down a power plant or shutting off the fuel supply. They are automation’s brain.
Perera’s article has been read by some as getting the utilities off the hook. But it doesn’t do that: Perera’s piece is not only well-researched and argued but also warns against complacency and ignoring the threat.
John Savage, emeritus professor of computer science at Brown University, says, “I perceive that the risk to all business is not changing very much. But to utilities, it is rising because it appears to be a new front in [Russian President Vladimir] Putin’s campaign to threaten Western interests. While I doubt that he would seek a direct conflict with us, he certainly is interested in making us uncomfortable. If he miscalculates, the consequences could be very serious.”
Samide warns against believing that all probes are equal in intent and purpose. He says there are various levels of probing from surveillance (checking on your operation) to reconnaissance (modeling your operation before a possible attack). Actual attacks, ranging from the political to the purely criminal, include ransomware attacks or the increasing cryptojacking in which a hacker hijacks a target’s processing power in order to mine cryptocurrency on the hacker’s behalf.
The threats are global and increasingly the attribution -- the source of the attack --concealed. Other tactics, according to Samide, include misdirection: a classic espionage technique for diverting attention from the real aim of the attack.
The existential question is if cyberwar goes from low-grade to high-intensity, can we cope? And how effective are our countermeasures?Today’s skirmishes are harbingers of the warfighting of the future.
Llewellyn King is executive producer and host of White House Chronicle, on PBS. His email is llewellynking1@kingpublishing.com. He's based in Washington, D.C. and Rhode Island.